Table of Contents
- Introduction:
- Components of Solar Photovoltaic:
- How Solar Photovoltaic Works:
- Equations for Photovoltaic:
- Calculator
- Applications for Solar Photo Voltaic:
- Limitations of Solar Photo Voltaic:
- The Limitations of Solar Photovoltaic Cells:
- Conclusion:
Introduction:
Solar Photovoltaic is an increasingly popular form of renewable energy, with the potential to provide clean, reliable energy to the world. Solar energy is energy from the sun that is converted into thermal or electrical energy. Every day, 173,000 terawatts of solar energy continuously reach the earth making it the most abundant renewable energy source available, and the U.S. has some of the richest solar resources in the world. Solar energy is harnessed through solar photovoltaic technology.
Components of Solar Photovoltaic:
Solar photovoltaic technology is a complex system that consists of several essential components. The most important components of this system are the solar PV array, a charge controller, a battery bank, an inverter, a utility meter through which the standalone solar PV will be connected to an electric grid.
The solar PV array is made up of several components, such as solar cells, framing, and glass, which work by collecting and harnessing photovoltaic energy from the sun.
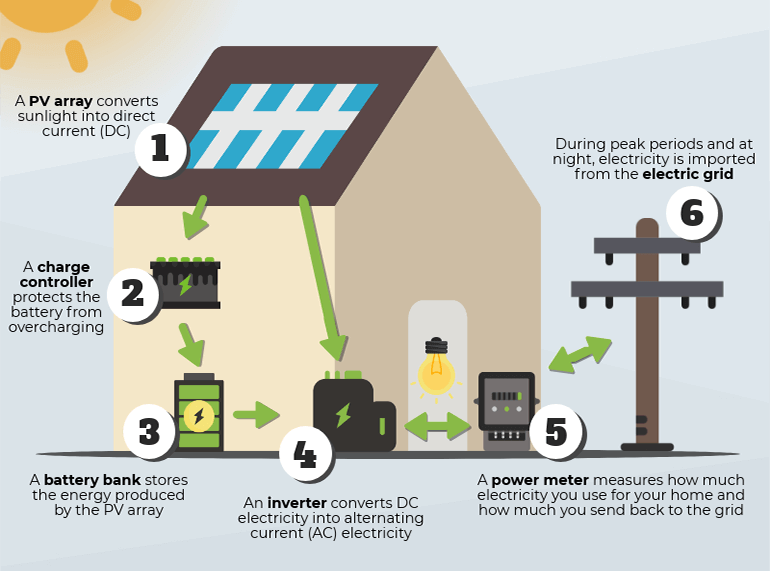
The charge controller is used to protect against electrical overload, overcharging, and may protect against overvoltage.
The battery bank is used to store energy generated by the solar panels.
The inverter is used to convert the direct current (DC) energy generated by the solar cells into alternating current (AC) energy that can be used by household appliances.
The utility meter is used to measure how much energy is being generated and used.
Finally, the connected electric grid is used to receive any excess energy generated by the system to the utility company.
How Solar Photovoltaic Works:
Solar Photo Voltaic (PV) is an alternative energy system that can convert sunlight directly into electricity. PV cells are made out of layers of semiconductor material, usually silicon, which absorb the sun’s rays or photons and knock electrons off the silicon atoms and generate direct current (DC). The DC generated by the cells is transferred to an inverter which then converts it to alternating current (AC). This is how a PV cell produce electricity. AC can be used to power appliances in homes and businesses.
The amount of electricity generated by a PV cell is determined by its size, number of cells, efficiency rating, and the intensity and angle of incoming sunlight. When multiple solar PV cells are connected together they form a panel that can produce more electricity than one single cell would generate alone. By combining several panels together into a larger array even more electricity can be produced. Arrays are often installed on roofs or other open surfaces that receive plenty of sunlight throughout the day.
Equations for Photovoltaic:
The equation used as a global standard to estimate the electricity generated by a photovoltaic system is given below
E = A x r x H x PR
Where
E = Energy (kWh)
A = total Area of the panel (m²)
r = solar panel yield (%),
H = annual average solar radiation on tilted panels
PR = Performance ratio, constant for losses (range between 0.5 and 0.9, default value = 0.75).
Calculator
Photovoltaic Panel Electricity Calculator
Electricity Generated: kWh
This equation relies on various factors such as the solar panel yield of a PV module, renewable energy, photovoltaics, energy yield simulations, the solar resource, the non-ideal diode equation, and equivalent circuit models for PV cells. All of these components are essential for accurately calculating the amount of electricity that can be generated from photovoltaics. The matrix-vector-formulation of the governing equations is also used to further refine the predictions and ensure the accuracy of the results. Photovoltaics is an important part of the renewable energy mix and the equations used to calculate its output is an essential step in making sure its potential is realized.
Applications for Solar Photo Voltaic:
1. Solar Farms: Solar farms are large-scale systems made up of thousands of photovoltaic (PV) panels that are used to generate electricity. These systems are usually connected to the grid, allowing the generated electricity to be used by the community. Solar farms are typically found in sunny areas with a lot of open land and can provide utility-scale power, ranging from tens of megawatts to more than a gigawatt of electricity.
2. Remote Locations: In areas where it is not cost-effective or possible to extend power lines, PV can be the perfect solution. Remote homes, villages in developing nations, lighthouses, offshore oil platforms, desalination plants, and remote health clinics can all benefit from PV-generated electricity.
3. Stand-Alone Power: In urban or remote areas, PV can power stand-alone devices, tools, and meters. PV can provide electricity for parking meters, temporary traffic signs, emergency phones, radio transmitters, water irrigation pumps, stream-flow gauges, remote guard posts, and lighting for roadways.
4. Power in Space: Photovoltaics have been a primary power source for Earth-orbiting satellites from the beginning. High-efficiency PV has supplied power for ventures such as the International Space Station and surface rovers on the Moon and Mars.
5. Building-Related Needs: PV panels mounted on roofs or ground can supply electricity. PV material can also be integrated into a building’s structure as windows, roof tiles, or cladding to serve a dual purpose. In addition, awnings and parking structures can be covered with PV to provide shading and power.
6.Military Uses: Thin-film photovoltaics (PV) are advantageous in situations where portability or durability are paramount because of their light weight and flexibility. Lightweight PV allows soldiers to charge electronics in the field or at remote locations.
7. Transportation: Vehicles like cars and boats can benefit from having PV as a backup power source. PV can be installed in car sunroofs to provide constant electricity or to charge the car’s batteries very slowly. Lightweight PV can be molded into the shape of airplane wings to aid in the propulsion of aircraft at great altitudes.
Limitations of Solar Photo Voltaic:
Solar photovoltaic (PV) cells have some limitations that need to be taken into consideration before investing in this type of energy source.
One of the main drawbacks is intermittent energy supply, as solar PV cells only produce energy when there is adequate sunlight.
In addition, they require a large area to be installed and are easily damaged. Furthermore, solar PV cells have a low efficiency and capacity utilization factor, resulting in less reliable power options and additional investments.
The Limitations of Solar Photovoltaic Cells:
1. Intermittency Issues: Solar photovoltaic cells are intermittent sources of energy, meaning they are not always available for converting into electricity. This is especially true during night-time, cloudy or rainy weather.
2. Less Reliable: The intermittency and unpredictability of solar energy make it a less reliable power solution.
3. Hight Initial Investments: The installation of a solar PV system requires an high initial investment as they require inverters and storage batteries.
4. Uses a Large Area: Solar PV systems require a large area of land or rooftop for installation.
5. Easily Damaged: Solar PV cells can be easily damaged and require additional insurance coverage to protect the investment.
6. Limited Availability: The optimum solar energy is only available in certain geographic regions and is not available in all locations.
Conclusion:
All in all, solar photo voltaic technology is a viable and rapidly advancing sector of renewable energy. It provides an ideal solution to many of the challenges posed by climate change, from reducing emissions to increasing access to clean energy. With continued research, solar PV could become even more efficient and cost-effective in the near future. Governments and businesses should invest in this technology now to ensure that it is well-positioned for life after fossil fuels.

Pingback: Battle of the Energies: Solar Energy vs. Wind Energy - Electrical Blog