Table of Contents
- Introduction to SCADA Systems
- Typical SCADA System Architecture
- Functions of SCADA in Power Distribution
- SCADA Software for Power Utilities
- Benefits of SCADA in Electrical Distribution
- Challenges and Considerations in SCADA Implementation
- Conclusion and Future of SCADA in Power Systems
In the realm of modern power systems, the SCADA system stands as a cornerstone technology, ensuring the reliable and efficient delivery of electricity. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of SCADA, specifically focusing on its critical role in power system operations. We will explore the fundamental principles, key components, and the evolution of SCADA systems, highlighting their importance in maintaining grid stability and optimizing power distribution.
Introduction to SCADA Systems
What is SCADA?
SCADA stands for supervisory control and data acquisition. It is a control system architecture that uses computers, networked data communications, and graphical user interfaces for high-level process supervisory management but uses other peripheral devices such as programmable logic controllers and discrete proportional-integral-derivative controllers to interface to the industrial process plant or equipment. SCADA systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes; these processes can be located locally or at remote locations.
Importance of SCADA in Power Systems
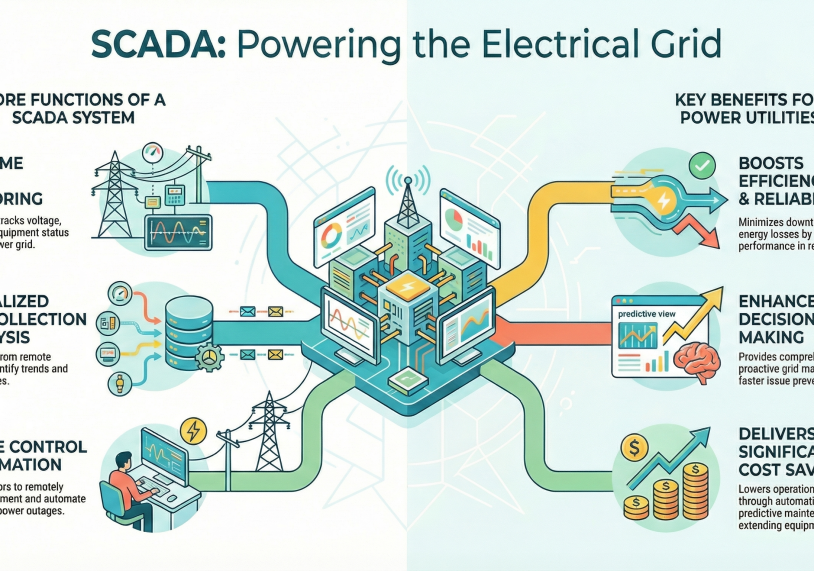
SCADA systems play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of electrical distribution and transmission. Using SCADA, operators can monitor and control equipment in real-time, from power plants to substations. The importance of SCADA in power system networks lies in its ability to collect data from remote terminal units (RTUs) and sensors, providing a centralized system view of the power grid. This enables quick responses to changing conditions, minimizing downtime and optimizing power factor.
History and Evolution of SCADA
The history of SCADA systems reveals a transition from manual, localized control to sophisticated, centralized automated systems. Early versions of supervisory control and data acquisition systems relied on simple telemetry and direct manual intervention. Over time, SCADA technology has evolved, integrating programmable logic controllers (PLCs), advanced communication protocols, and sophisticated SCADA software. Modern SCADA systems offer enhanced data collection, improved security, and the ability to analyze historical data to optimize power generation and power supply within the power distribution system.
Typical SCADA System Architecture
Components of SCADA
A typical SCADA system architecture consists of several key components working together. These components include Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), which interface with the industrial plant or equipment. SCADA in power systems includes communication networks that transmit real-time data to a central supervisory control system. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) are essential for operators to monitor and control the power distribution system effectively. Key components are:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| RTUs and PLCs | Interface with industrial plant/equipment |
| Communication Networks | Transmit real-time data to a central control system |
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) are essential for operators to monitor and control the power distribution system effectively.
How SCADA Systems Interact with Power Distribution
SCADA systems interact with power distribution by providing a centralized system for monitoring and control of electrical distribution networks. Using SCADA, operators can monitor and control equipment at substations and along the power grid in real-time. The system collects data from RTUs and sensors, allowing for immediate responses to any anomalies or changes in power system conditions. SCADA solutions enable efficient power distribution and optimization of power factor.
Data Flow in SCADA Systems
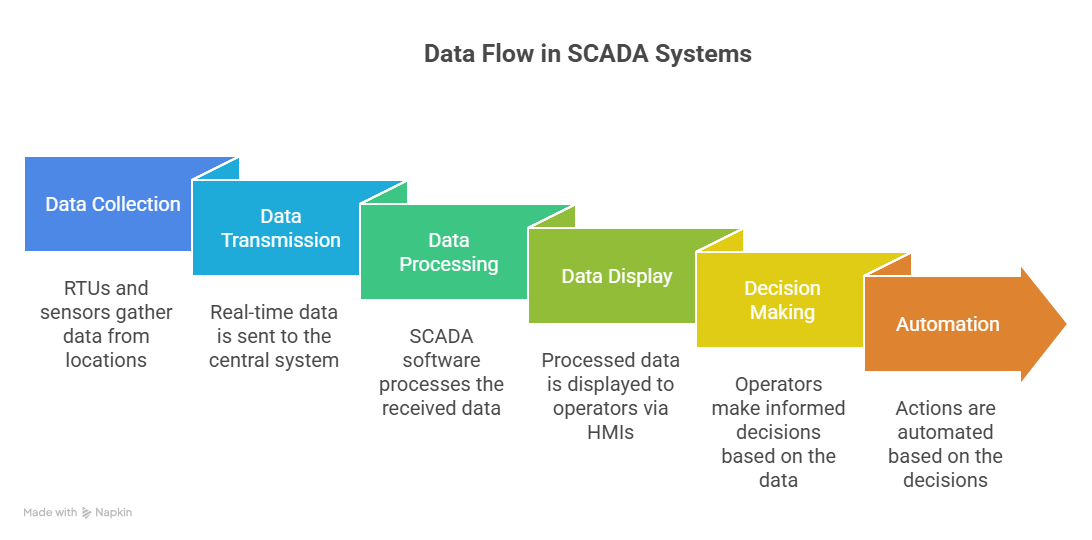
Here’s how data flows in a SCADA system, which involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: RTUs and sensors gather data from different locations, such as within the power system network and the industrial plant.
- Data Transmission: This real-time data is then sent to the central SCADA system using communication networks.
Following transmission, the SCADA software then processes the data, displaying it to operators via HMIs for informed decisions and automation. This structured flow facilitates effective control and monitoring.
Functions of SCADA in Power Distribution
Real-time Monitoring
One of the primary functions of SCADA in power distribution is real-time monitoring of the power grid. SCADA systems are used to continuously monitor equipment, power plants, and substations, providing operators with up-to-the-minute data on system conditions. This real-time data includes voltage levels, current flows, and equipment status. SCADA technology enables operators to quickly identify and address any issues, minimizing downtime and ensuring reliability of power supply.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection and analysis are critical functions of SCADA systems. SCADA collects data from various points in the power distribution system using RTUs and sensors. This data is then analyzed to identify trends, anomalies, and potential issues. SCADA in power helps utilities optimize power generation and power distribution, improve efficiency, and ensure stable power supply. Historical data analysis supports predictive maintenance and enhances long-term grid performance.
Control Operations and Automation
SCADA facilitates control operations and automation, enabling operators to remotely manage and control equipment. Using SCADA, operators can adjust voltage levels, switch circuits, and manage power factor to optimize the performance of the power system network. Automation features in modern SCADA systems allow for automated responses to predefined events, such as automatic switching to backup power sources during outages. This automation enhances system reliability and reduces the need for manual intervention.
SCADA Software for Power Utilities
Types of SCADA Software Solutions
SCADA software solutions for power utilities vary, catering to different needs within the power system network. Some solutions focus on real-time monitoring and control, providing operators with a comprehensive overview of the power grid. Others emphasize data collection and analysis, helping utilities optimize power generation and power distribution. Understanding the different types of SCADA systems used allows utilities to select a system that aligns with their specific operational requirements and grid management goals.
Key Features of SCADA Software
Key features of SCADA software are multifaceted. They include several critical components, notably:
- A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) for intuitive operation
- Robust communication protocols for real-time data transfer
These, alongside advanced data analysis tools, enable operators to effectively monitor and control the electrical distribution system. The ability to collect data from RTUs and sensors and automate responses is crucial for maintaining grid reliability. Furthermore, modern SCADA systems offer enhanced security features to protect against cyber threats, ensuring a stable power supply.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integration with existing systems is vital for the effectiveness of SCADA systems. SCADA software must seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs), remote terminal units (RTUs), and other control equipment. Effective integration ensures that real-time data flows smoothly, allowing operators to monitor and control the power distribution system without disruption. Proper integration also facilitates the modernization of older power plants, enabling them to leverage the benefits of a modern SCADA.
Benefits of SCADA in Electrical Distribution
Improved Efficiency and Reliability
SCADA systems play a crucial role in improving the efficiency and reliability of electrical distribution. Using SCADA allows for real-time monitoring and control of equipment, ensuring optimal performance of the power grid. SCADA in power enables operators to quickly detect and respond to anomalies, minimizing downtime and enhancing the reliability of power supply. Furthermore, data collection and analysis capabilities help utilities optimize power factor and reduce losses in the power distribution system, improving overall efficiency.
Enhanced Decision Making
SCADA enhances decision-making by providing operators with comprehensive real-time data and analytical tools. The ability to collect data from various points in the power system network and analyze trends allows for informed decisions regarding power generation and power distribution. Operators can use SCADA to proactively manage the grid, preventing potential issues and optimizing performance. SCADA solutions provide the insight needed for efficient and effective grid management, improving overall system reliability.
Cost Savings for Utilities
Cost savings for utilities are a significant benefit of implementing SCADA systems. SCADA systems are used to optimize power generation and distribution, reducing energy waste and improving efficiency. By automating processes and minimizing downtime, SCADA helps utilities lower operational costs and extend the lifespan of equipment. Additionally, the ability to collect data and perform predictive maintenance reduces the need for costly repairs and replacements, resulting in long-term cost savings for power distribution and the industrial plant.
Challenges and Considerations in SCADA Implementation
Cybersecurity Risks
One of the paramount challenges in SCADA implementation is addressing cybersecurity risks. Modern SCADA systems, with their reliance on networked communication, are increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats that can compromise the reliability of the power system network. Protecting the industrial plant and electrical distribution system from unauthorized access and malicious attacks requires robust security measures, including encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. Implementing comprehensive cybersecurity protocols is essential to safeguard SCADA in power and ensure uninterrupted power supply. With proper implementation, utilities can mitigate the risk.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Scalability and future-proofing are critical considerations for SCADA implementation. As the power grid evolves and expands, the SCADA system must be able to adapt and accommodate increasing data volumes and additional equipment. A scalable SCADA architecture ensures that the power system can continue to monitor and control operations effectively, even as the network grows. Future-proofing involves selecting SCADA software and system components that can be upgraded and integrated with emerging technologies, such as smart grid solutions and advanced automation capabilities to optimize power generation.
Training and Skill Development
Effective training and skill development are essential for the successful implementation and operation of SCADA systems. Power system operators and maintenance personnel require comprehensive training on SCADA software, system components, and control system protocols. Proper training ensures that operators can effectively monitor and control the electrical distribution system, respond to emergencies, and perform routine maintenance tasks. Investing in ongoing training programs helps to maintain a skilled workforce capable of maximizing the benefits of SCADA technology and ensuring power grid reliability.
Conclusion and Future of SCADA in Power Systems
Trends in SCADA Technology
The trends in SCADA technology point towards greater integration with cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and enhanced cybersecurity measures. Cloud-based SCADA solutions offer improved scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. AI-powered data analytics enable predictive maintenance and optimized power distribution. The use of advanced encryption and intrusion detection systems enhances the security of SCADA in power, protecting against cyber threats and ensuring a stable power supply. Modern SCADA systems are evolving to meet the demands of the power system network.
The Role of SCADA in Smart Grids
SCADA plays a crucial role in smart grids by enabling real-time monitoring, control, and automation of power distribution. Smart grids utilize SCADA systems to optimize power generation and power supply, manage distributed energy resources, and improve grid reliability. SCADA facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the power system network. SCADA solutions allow for better power factor management, reduced energy waste, and enhanced grid stability. SCADA is integral to achieving the goals of smart grids by ensuring efficient and resilient power distribution.
Final Thoughts on SCADA in Power Systems
In conclusion, SCADA systems are indispensable for the efficient and reliable operation of modern power systems. SCADA enables real-time monitoring, data collection, and control operations, ensuring stable power distribution and optimized power generation. As power systems continue to evolve, SCADA technology will play an increasingly critical role in enhancing grid reliability, improving efficiency, and facilitating the transition to smarter, more resilient power grids. Embracing modern SCADA solutions is essential for utilities seeking to meet the growing demands for power supply.